Overview
Cron is the time-based job scheduler in Unix-like computer operating systems.
Cron enables users to schedule jobs (commands or shell scripts) to run periodically at certain times or dates.
It is commonly used to automate system maintenance or administration, though its general-purpose nature means that it can be used for other purposes.
General Information
To edit the Cron Table use:
crontab -e
To view the Cron Table use:
crontab -l
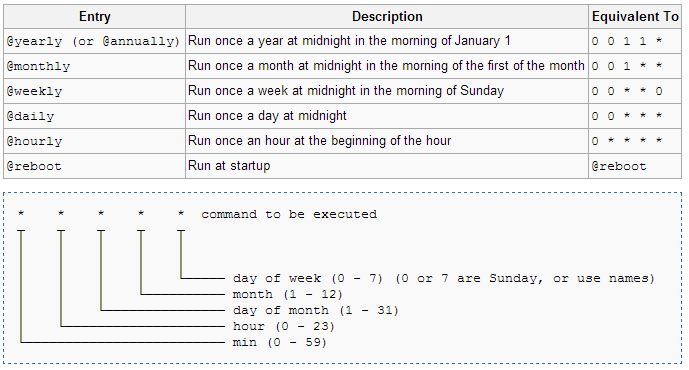
The crontab file
| Minute | Hour | Day of Month | Month | Day of Week | Command |
| (0-59) | (0-23) | (1-31) | (1-12 or Jan-Dec) | (0-6 or Sun-Sat) |
Using Cron Examples
Run ‘check.sh’ script every 3 Minutes :
*/3 * * * * /scripts/check.sh
Run ‘check.sh’ script every Day at 07:00 :
0 7 * * * /scripts/check.sh
Run ‘check.sh’ script every 24th of the Month at 13:10 :
10 13 24 * * /scripts/check.sh
Run ‘check.sh’ script every Sunday at 21:53 :
53 21 * * 0 /scripts/check.sh
Additional Info
Adding Environment Variables :
Cron doesn’t export any of the profile files,
so if you need a path variable you can set it in crontab (using crontab -e) :
PATH=$PATH:/sbin:/bin/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/scripts
0 * * * * root /scripts/check.sh
Output your command to a log file :
0 * * * * /sbin/ping -c 10.0.0.1 >> /scripts/cron.log
Run as a different user (for example root) :
0 * * * * root /scripts/check.sh
DevOps/IT Specialist, Musician.
IT Manager – Faculty of Exact Sciences, Bar-Ilan University
Personal Website
