centos gunicorn installation instructions
centos gunicorn
centos gunicorn : In this simple tutorial I’ll explain how to install and run Gunicorn python server on your CentOS machine.
This tutorial is meant for Centos 6.4 and above but it should work on any CentOS 6.x release.
What is gunicorn?
From: Gunicorn – Python WSGI HTTP Server for UNIX:
Gunicorn ‘Green Unicorn’ is a Python WSGI HTTP Server for UNIX. It’s a pre-fork worker model ported from Ruby’s Unicorn project. The Gunicorn server is broadly compatible with various web frameworks, simply implemented, light on server resources, and fairly speedy.
Installation
Python
before you going to install the centos gunicorn server you need to insure you have the python interperter installed (it should be, as it’s installed by default on the latest CentOS releases). to check that you have python use the command:
python
command not found of course means you need to install python now.
Install python
first make sure your have python installed. Simple as:
yum install python
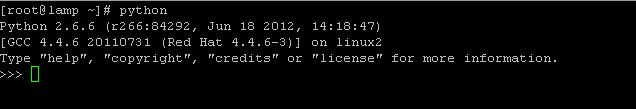
test python by typing: “python” and you should see something similar to:
(Ctrl+D to exit)
Gunicorn
Next we need to install gunicorn. for this we have (as always) several choices.
1) Using YUM. I personally don’t recommend it. I know some are happy to use the system packaging management wherever possible, but as for python I don’t think it’s the way to go.
To install gunicorn using yum:
yum install python-gunicorn
2) Using easy_install. using easy_install is a better choice for my taste to install python packages. this is how you install gunicorn using easy_install, but I recommend installing gunicorn using PIP as I will show next…
yum install python-setuptools easy_install gunicorn
3) Using PIP: This is my RECOMMENDED way of installing gunicorn. to install PIP you actually need easy_install so the commands are:
yum install python-setuptools easy_install pip pip install gunicorn
Virtualenv
I can’t recommend enough to start working with virtualenv from beginning. At some point in the future, if you are going to consist with python coding, you are going to use the ‘pip update’ command to update some or all your libraries and then expect your python application to stop working.
Python libraries, as any open source library, have the freedom to sacrifice backward compatibility for new features, performance or redesign.
Virtualenv is a python virtual environment tool to ensure that your python applications will work as expected as long you don’t deliberately update some or all of the dependency libraries for that virtual environment specifically.
To install virtualenv (and virtualenvwrapper) and learn the basics read this tutorial. then create your virtual environment and install gunicorn to that environment.
# after you've install pip, virtualenv and virtualenvwrapper mkproject myapp workon myapp pip install gunicorn
Running Gunicorn
Basic usage:
$ gunicorn [OPTIONS] APP_MODULE
so for the following myapp.py file:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -
def app(environ, start_response):
data = 'Hello, World!\n'
status = '200 OK'
response_headers = [
('Content-type','text/plain'),
('Content-Length', str(len(data)))
]
start_response(status, response_headers)
return iter([data])
just run:
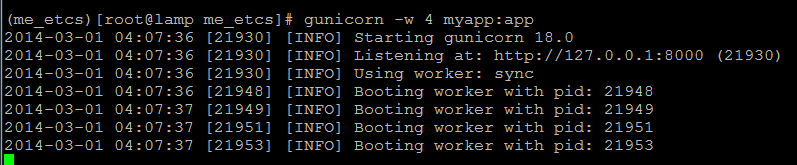
gunicorn -w 4 myapp:app
# Sample output [INFO] Arbiter booted [INFO] Listening at: http://127.0.0.1:8000 [INFO] Worker spawned (pid: 16801) [INFO] Worker spawned (pid: 16802) [INFO] Worker spawned (pid: 16803) [INFO] Worker spawned (pid: 16804)
This command starts gunicorn with 4 workers on port 8000. feel free to experiment and customize the command with additional parameters.
There also command line for using Django <1.4 and Paster. read more here.
Read more about configuring Gunicorn and configuration files.
Deploying Gunicorn
on deployment, It’s strongly recommended to use Gunicorn behind a proxy server.
nginx
I personally prefer nginx but it’s not your only choice.
If you want to install nginx on your CentOS machine follow this installation instructions.
use this script (at github) to configure your nginx to pass request to the gunicorn process
Monitoring and Logging
Usally you’d want the gunicorn to be run in the background, load on boot and restart on errors. you want also the ability to monitor that process.
There are several tools for that.job, including: Supervisord, Gafferd, runit and many more… choose what fits you best. here you have examples for monitoring gunicorn using those tools.
That it. enjoy playing with your centos gunicorn setup.